MongoDB Integration for Token Management and Email Analysis Caching
- Published on
- /3 mins read/---
Implementing a robust and efficient database system for token management and caching requires careful consideration of data structure, performance, and security. This article explores our MongoDB integration, focusing on how we handle token management and implement a two-tier caching system for email analysis results.
MongoDB Integration
Overview
This document describes the MongoDB integration in our application, focusing on user management and email analysis caching.
Database Structure
Collections
users
- Stores user information and authentication state
- Unique index on email field
{ email: String, // User's email (unique index) name: String, // User's display name picture: String, // User's profile picture URL created_at: Date, // Account creation timestamp last_login: Date, // Last login timestamp is_active: Boolean, // User active status last_sync_time: Date // Last email sync timestamp }email_analysis_cache
- Stores email analysis results
- Permanent storage for analysis data
{ message_id: String, // Email message ID (unique index) cached_at: Date, // Cache timestamp (for tracking) result: { subject: String, // Email subject sender: String, // Email sender date: String, // Relevant date status: String, // Job application status company: String, // Company name position: String, // Position title details: String, // Additional details confidence: Number, // Analysis confidence score message_id: String // Email message ID }, }
Indexes
users Collection
// Unique index on email
db.users.createIndex({ email: 1 }, { unique: true })email_analysis_cache Collection
// Unique index on message_id
db.email_analysis_cache.createIndex({ message_id: 1 }, { unique: true })
// Index on cached_at for tracking purposes
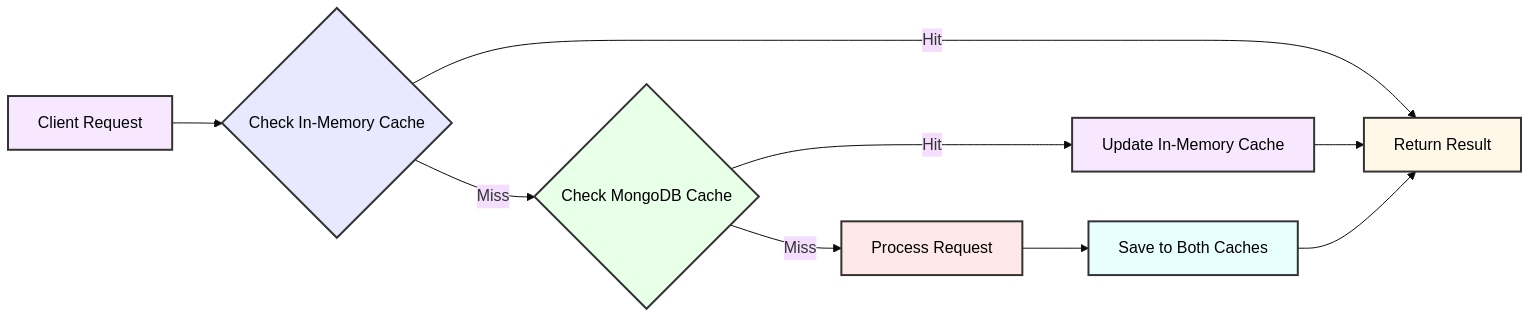
db.email_analysis_cache.createIndex({ cached_at: 1 })Two-Tier Caching Architecture
TTLCache (First Layer)
- Thread-safe memory cache
- Automatic expiration
- Size-limited cache
# Token cache configuration token_cache = TTLCache( maxsize=MAX_TOKEN_CACHE_SIZE, # 1000 items ttl=TOKEN_CACHE_TTL, # 1 hour ) # Analysis cache configuration analysis_cache = TTLCache( maxsize=MAX_ANALYSIS_CACHE_SIZE, # 1000 items ttl=ANALYSIS_CACHE_TTL, # 7 days )MongoDB (Second Layer)
- 360-day TTL for email analysis
- Persistent storage for user data
- Automatic cleanup of old analysis results
Token Management
Access Token
- Stored in TTLCache (memory only)
- 1-hour TTL
- Used for Gmail API access
Refresh Token
- Stored in HttpOnly cookie
- 30-day expiration
- Used to obtain new access tokens
- Not stored in MongoDB
Session Token
- JWT format
- Stored in client localStorage
- Contains user information
- 24-hour expiration
Performance Optimization
Indexing Strategy
- Unique indexes for fast lookups
- TTL indexes for automatic cleanup
- Compound indexes where needed
Query Optimization
- TTLCache reduces DB load
- Thread-safe operations
- Batch operations for multiple documents
Resource Management
- Automatic cleanup of old data
- Connection pooling
- Asynchronous operations
